METHODS OF MEASUREMENT OF NATIONAL INCOME | Mumbai University 2021-22
What is National Income explain the METHODS OF MEASUREMENT OF NATIONAL INCOME
National Income
- The modern economy is a money economy. Hence, the national income of a country is expressed in terms of money. The total income of the nation is called national income.
- In simple words, national income is “The total money value of all the goods and services produce in an economy during a given period”.
- National Income is also the total income earned by factors. National Income is “the net money value of commodity and services flowing during the year from the country productive system in the hand of the ultimate consumer”.
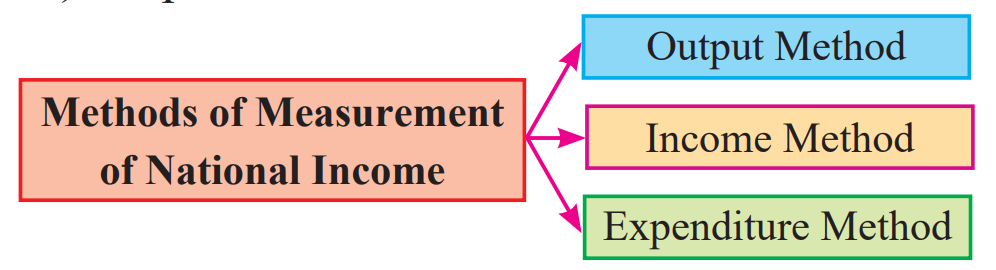
METHODS OF MEASUREMENT OF NATIONAL INCOME
For measuring national income, the economy through which people participate in economic activities, earn their livelihood, produce goods and services and share the national products is viewed from three different angles :
- The national economy is considered as an aggregate of producing units combining different sectors such as agriculture, mining, manufacturing, trade and commerce, etc.
- The whole national economy is viewed as a combination of individuals and households owing different kinds of factors of production which they use themselves or sell factor services to make their livelihood.
- The national economy may also be viewed as a collection of consuming, saving and investing units (individuals, households and government).
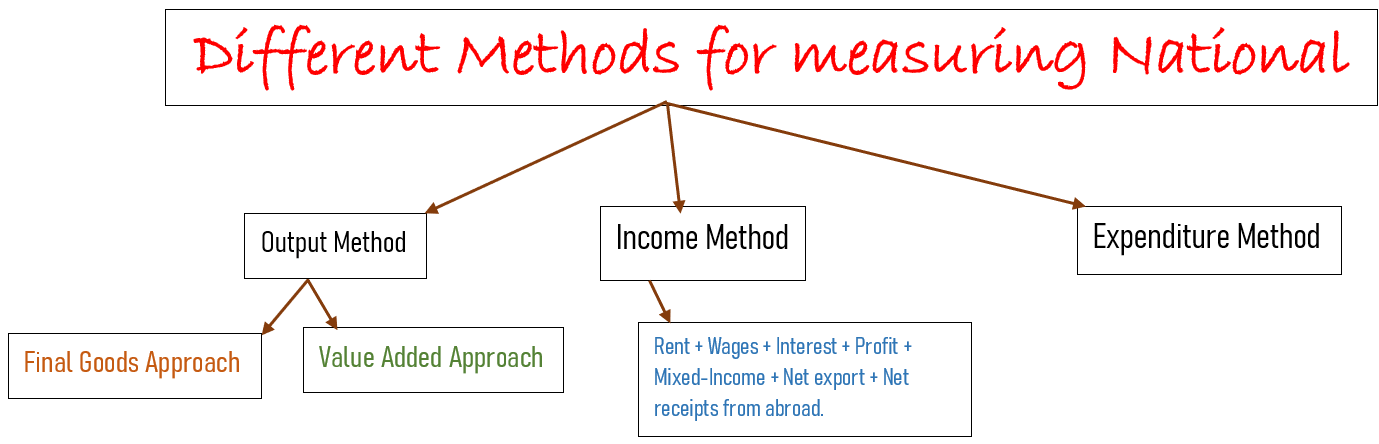
There are three methods for measuring national income.
- Value-added Method
- Income Method
- Expenditure methods.
There are three methods of measuring national income.
- Output Method/Product Method
- Income Method
- Expenditure Method
NET OUTPUT OR VALUE ADDED METHOD
This method of measuring national income is also known as product method, inventory method, or Value Added Method. It consists of three stages:
- estimating the gross value of domestic output in the different branches of production
- determining the cost of material and services used and also the depreciation of physical assets
- subtracting these costs and depreciation from gross value to obtain the net value of domestic output.
According to this method, the economy is divided into various sectors, like agriculture, mining, manufacturing, small enterprises, commerce, transport, communication, and other services.
The output or product method is followed either by valuing all the final goods and services, produced during a year, at their market price or by adding up all the values at each higher stage of production, until these products are turned into final products.
Precautions:
- To avoid double counting, only the value of final goods and services must be taken into account.
- Depreciation of capital assets should be deducted.
- Value of exports should be added and value of imports should be deducted.
- Sale and purchase of second-hand goods should be ignored as it is not a part of current production.
- Goods used for self-consumption by farmers should be estimated by guess work.
- It includes only those goods and services which are exchanged for money
Income Method:
This method of measuring national income is also known as factor cost method. National Income is obtained by adding income such as rent, interest, wages, etc. by all the persons and enterprises in the country during a given period.
Wherever goods and services are produced in the economy, income is also generated and distributed among the factors of production. Different factors of production are paid for their productive services. Thus, labour gets wages, the land gets rent, capital gets interest, and the entrepreneur gets profits. Thus, GNP, according to the income method, is calculated as follows:
- NI = Rent + Wages + Interest + Profit + Mixed Income + Net export + Net receipts from abroad.
NI = R + W + I + P + MI + (X–M) + (R–P)
So it includes:
- Rent: Total rent includes, rent of land, shop, factory, etc.
- Wages and Salary: Total wages and salary earned through productive activity.
- Interest: Interest on capital received by an individual.
- Profit of enterprise.
- Net income earned from abroad.
Precautions:
- Transfer payments like pensions, gifts, donations, gains from gambling and lotteries, etc. are to be excluded.
- All unpaid services of house-wife, and the help of friends should be excluded.
- Any income from the sale of second-hand goods like a car, house, etc., should be ignored.
- Net income from abroad should be included.
- Undistributed profit of the company, government income, and profit of government should be included.
Expenditure Method:
Under this method, national income is measured by adding all the expenses made on the purchase of goods and services. We include the expenditure of the following category.
- Consumption (C):- Private Final Consumption Expenditure (C) by households is the market value of all consumer goods like food, transport services, medical services, gold, house, etc.
- Investment (I):- It refers to expenditure made by private businesses on replacement, renewals, and new investment (I), like machinery, tools, factories, buildings, etc.
- Government Expenditure (G):- expenditure incurred by the government on various administrative services like law and order,
defence, education, health, etc., and expenditure incurred by the government, on creating infrastructural facilities like the construction of roads, railways, bridges, dams, and canals, which are used by the business sector for the production of goods and services in any economy (G). - Net Income from abroad (x-m):- It refers to the net difference between export and import.
- Net Receipts (R-P): The difference between the expenditure incurred by foreigners on domestic goods and services (R) and expenditure incurred abroad by residents on foreign goods and services (P).
In estimating the total national expenditure, any of the two following methods are follows; First, all the money expenditures at market price are computed and added up together, and Second, the value of all the products finally disposed of are computed and added up, to arrive at the total national expenditure.
The items of expenditure which are taken into account under the first method are Private consumption expenditure; Direct tax payments; 18 Payments to the non-profit making institutions and charitable organizations like schools, hospitals, orphanages, etc., Private savings.
Under the second method, the following items are considered Private consumer goods and services; Private investment goods; Public goods and services; Net investment abroad. The second method is more extensively used because the data required in this method can be collected with greater ease and accuracy.
Precautions:
- Expenditure on all intermediate goods and services should be ignored, to avoid double counting.
- Expenditure on the repurchase of second-hand goods should be ignored, as it is not incurred on currently produced goods.
- Indirect taxes should be deducted.
- Expenditure on final goods and services should be included.
- Subsidies should be included.
SYBCOM Business Economics Notes Click HERE
Reference: shaalaa.com, Maharashtra Board Book