TYBCOM Sem 5 Commerce notes pdf Mumbai University
TYBCOM Sem 5 Commerce notes pdf | Commerce Semester 5 notes Mumbai University
Chapter 1:Human Resource Management
Q.1)Explain Human Resource Management and its features.
- HRM is a process of managing the human resources of the organization. Human Resource Management, is like a company’s ‘people’ department. HRM is responsible for everything related to employees, from hiring them to letting them go. HRM is important because it helps both the employees and the company.
- For example, when a company uses HRM to hire the right people, it ensures that the employees are happy and do their job well. And when someone has to leave the company, HRM makes sure it’s done fairly and nicely, so everyone is treated well.”
- Process: HRM is a process of managing people in such a manner that helps an organization achieve its goals. It covers everything from hiring employees to managing their performance and, terminating their employment. For example, When a company decides to expand its operations, HRM is responsible for hiring new employees, providing them training etc.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: HRM involves various disciplines to manage the workforce efficiently. It includes psychology, sociology, communication, and aspects of workforce management.
- Universal Application: HRM is essential not only for businesses but also for non-business organizations. HRM are needed in non-business organisations, like in college or university selection, training and motivating their staff is required.
- Continuous in Nature: HRM is an ongoing process that continues as long as the organization exists. It includes activities like recruitment, training, and promotions.
- Long-Term Benefits: HRM provides long-term benefits to employees, organizations, and society as well. Giving training to improve the skills and knowledge of employees and properly guiding them in their work makes them a long-term asset to the organization.
- Development of Employees Efficiency: HRM involves training, motivating, career planning, and promoting, these types of things helps organizations to get the best of their employees as much as possible.
Q.2) Functions of HRM:
- Human Resource Planning: HRM involves Human Resource Planning (HRP), HRP is the process of identifying the required manpower in terms of both quantity and quality for business activities.
- Selection: HRP helps identify the required workforce, while the selection process finds the right individuals who can perform their work effectively. The “right” workforce includes people with the necessary knowledge and skills for a particular job.
- Placement: Placement comes after the selection process. Selection identifies the right people for the business, placement ensures that these individuals are assigned to the appropriate positions based on their skills and knowledge.
- Performance Appraisal: Performance Appraisal is a systematic evaluation of employees, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. It helps organizations recognize the right employees for promotions, training, transfers, and other activities that benefit both the business and the workforce in terms of career development.
- Promotion: Under HRM, managers should provide recognition and rewards to employees who perform well. It motivates them to do even better.
- Training and Development: Based on performance appraisals, organizations identify employees’ strengths and weaknesses and provide them with training to enhance their skills and knowledge.
- Compensation Function: Employees must be rewarded and recognized for their performance. Under HRM, managers use both monetary and non-monetary methods to increase employee efficiency and motivation.
Steps involves in HRP are as follow:
- Review Organizational Goals: The first step in HRP is to review what the organization wants to achieve. This helps figure out how many people are needed to do the tasks the company plans to do.
- HR Requirements Forecast: HR managers predict how many and what kind of people the organization will need based on its goals. The requirement of human resources considers in terms of quantity and quality.
- HR Supply Forecast: Under this HRD managers forecasts the availability of manpower. HRD managers either look for employees within the company or hire people from outside when they need more workers.
- Comparison: HR managers compare the number of people they need (from step 2) with the number of people available (from step 3). HRD managers compare both options to determine if they have enough workforce.
- No Differences: If the numbers from step 2 and step 3 are the same, then no action is needed. After the comparison of HR requirement and supply if managers get to know there is no difference in this number then no action required.
- Difference: If the required manpower is less or more than the supply of manpower, then managers will hire or fire the workforce as per the situation.
Q.4) Write about Job Analysis and its components.
- A job can be defined as the sum of all tasks, duties, and responsibilities assigned to an employee.
- Job Analysis refers to the process of studying and collecting all relevant information about a specific job.
- Job Analysis consists of two components : A)Job Description B) Job Specification
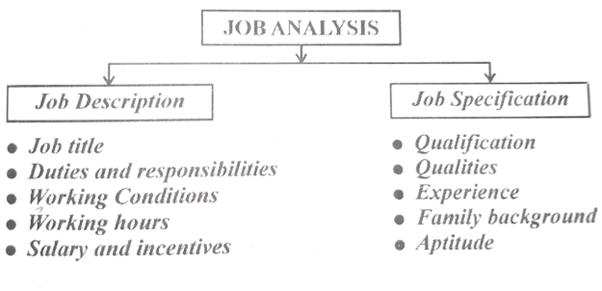
A) Job Description:
- A job description describes the job, including the job title, location, duties, and other relevant information about the overall job. Contents of a Job Description are:
- Job Identification: It provides information related to the job title, location, and department name, helping to identify the job.
- Duties and Responsibilities: It outlines the expected duties and responsibilities of employees, specifying what, how, and why of the job.
- Machines and Tools: It describes the types of machines, tools, and equipment used in performing job activities. Therefore, candidates who can handle these machines and tools will be considered for selection.
- Social Environment: This description helps applying candidates understand the social environment at the workplace.
- Working Conditions: It explains the working conditions, including Duration of breaks, Speed of work, Timing of shifts, etc.
B) Job Specification:
Job Specification provides details about the qualities, qualifications, gender, and other relevant criteria for selecting an employee.
- Mental Characteristics: This includes IQ level, aptitude, logical reasoning, and creativity among employee attributes.
- Personal Characteristics: It encompasses age, gender, education, and other relevant personal characteristics required of the employee.
- Physical Characteristics: This category covers height, health, vision, hearing, and other physical attributes necessary for the job.
- Social and Psychological Characteristics: Social and psychological qualities such as cooperativeness, interpersonal skills, and emotional stability are included in this section.
Q.5) Explain Recruitment and its sources.
Recruitment is the process of searching for and attracting candidates to apply for jobs. Sources of Recruitment are:
A) Internal Sources: These refer to sourcing applicants from within the company.
- Transfer: When there’s a need to fill a position, managers can do so by transferring existing employees.
- Promotion: Similarly, this method involves selecting employees from within the company and promoting them to higher positions. These individuals are typically more efficient and committed employees.
- Retirees: In this approach, the organization recalls retired employees for a shorter period to fill positions, rather than searching for new candidates.
- Internal Advertisements: This method involves posting vacancy ads on the company’s notice board or website for existing employees to apply for positions that interest them.
B) External Sources: These are ways to acquire candidates from outside of the organization.
- Consultants: Sometimes, firms may enlist the help of consultants for workforce recruitment.
- Campus Recruitment: The company’s recruitment committee visits various college campuses to search for capable employees for their jobs.
- Advertisements: Recruitment ads are also placed on websites and in other sources like newspapers to attract candidates.
- Recommendation: Recommendations from existing managers are also considered when recruiting candidates.
Chapter-2:HUMAN RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT
Q.1) Explain HRD and its Function.
- Human resource development involves activities aimed at developing the organization’s human resources. This includes training initiatives designed to enhance the skills and knowledge of the workforce.
- Additionally, it involves career development and organization development efforts, all of which serve to motivate employees and maximize their productivity.
- Training: Training is one of the most important components of HRD because it enables employees to acquire additional knowledge and valuable skills.
- Promotion: Promotion means offering employees higher positions and additional financial benefits. It serves as motivation for employees to deliver their best performance.
- Career Development: This involves assigning challenging tasks, providing training, mentoring, and other activities that offer long-term benefits to employees. These activities not only make employees better but also help the organization in finding and maintaining a skilled workforce.
- Motivation: Motivation plays an essential role in HRD as it empowers employees to be efficient and dedicated in their work. Rewarding and recognizing employees are effective ways to boost motivation, with rewards being both monetary and non-monetary.
- Performance Appraisal: It is a comprehensive process that provides a holistic analysis of an employee’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis). Performance appraisal assists the organization in various HRD activities, including training and promotion.
- Mentoring: Mentoring is a valuable method of providing training, especially for higher positions like executive roles. Typically, a mentor is a senior individual who shares personal experiences and knowledge, enhancing the decision-making and problem-solving abilities of the employee.
Q.2) Explain Training and its importance.
- Training is a planned program that provides employees with additional knowledge and skills to improve their performance.
- There is a slight difference between training and development: training is a short-term learning process, while development is a longer-term process that helps individuals acquire knowledge and skills.
Importance of Training and Development:
- Innovation: Training helps employees come up with new ideas and schemes, benefiting the organization by gaining a competitive advantage.
- Optimum Resource Use: Training ensures the best use of physical, capital, and labor resources. It reduces wastage and can lead to higher profits.
- Competitive Edge: Training results in highly productive employees who use resources efficiently, reducing costs and improving work quality, thus providing a competitive advantage.
- Efficient Workforce: Training allows employees to enhance their skills and knowledge, enabling them to work efficiently and effectively.
- Teamwork: Training improves employee knowledge, skills, and attitudes, fostering a cooperative attitude crucial for effective teamwork in organizations.
- Customer Satisfaction: Quality work resulting from training leads to higher customer satisfaction, as products meet customer expectations.
Q.3) Methods of Training and Development.
There are two primary methods of training: A) On-the-job and B) Off-the-job.
A) On-the-Job Training: On-the-job training means employees learn while they’re working at their actual job location. Here are some on-the-job training methods:
- Job Rotation: This involves moving employees from one job to another. For example, a cashier might be assigned to the accounting department. It reduces boredom and provides varied work experience.
- Understudy: Juniors are trained to perform the duties of their superiors because they are likely to take over those positions when the seniors retire, transfer, or get promoted.
- Mentoring: Mentoring is similar to training. A mentor, often a senior employee, guides their mentee (a junior employee) as a coach or guide.
- Coaching and Counseling: Seniors help improve the skills of juniors by giving them challenging tasks, enabling them to gain new experiences and skills.
- Planned Progression: Similar to job rotation, but after each job change, employees receive higher pay and promotions.
B) Off-the-Job Methods: In off-the-job training, employees are trained away from their workplace, incurring special costs for the manager. Here are some off-the-job training methods:
- Management Games: Trainers use management games to teach skills like problem-solving, teamwork, and communication.
- Role Playing: Trainees act out the roles of managers or employees, helping them gain experience and decision-making skills.
- Seminars and Workshops: In seminars, trainees present their work, guided by their superiors. Workshops involve interactive training with trainers helping trainees develop specific work skills.
- Case Studies: Managers use case studies to analyze people, events, decisions, etc., developing trainees’ decision-making abilities and providing knowledge about real situations and their solutions.
- Conferences: Conferences bring together many participants to discuss topics and the latest developments. Experts share their opinions, providing participants with valuable knowledge about these topics.
Q.4) Explain Performance appraisal and its benefits/uses.
- Performance appraisal is like a comprehensive review of an employee’s work, similar to a SWOT analysis. It helps with other HRD activities such as training, promotion, and transfers. It provides feedback to employees about their work.
- Here are the uses and benefits of performance appraisal:
- Training: Performance appraisal helps management understand whether an employee needs additional training or not. It indicates if the employee lacks certain skills or knowledge.
- Promotion: Performance appraisal provides information about an employee’s strengths, helping managers make decisions about promotions based on their abilities and skills.
- Transfer: When there’s a shortage of employees in another branch or department, or when an employee is a good fit for a different position, performance appraisal makes transfers smoother.
- Motivation: By describing an employee’s performance, performance appraisal identifies efficient workers who can receive monetary or non-monetary benefits, motivating them to perform better.
- Effective Communication: Performance appraisal facilitates effective communication between employees and employers, leading to improved performance.
- Performance Feedback: Performance appraisal offers feedback on an employee’s strengths and weaknesses. This feedback leads to better performance and more efficient output.
Q.5) Explain limitations of performance appraisal.
- Halo Effect: This happens when a performance appraisal is based on just one positive aspect of the person being rated. The rater might see one good quality and assume the person is excellent overall, ignoring other aspects.
- Horn Effect: This is the opposite of the Halo Effect. It occurs when one negative factor leads the rater to give an overall negative assessment, even if there are other positive aspects.
- Central Tendency: Some raters tend to give everyone average scores, whether they are performing well or not. This can result in a lack of differentiation between high and low performers.
- Leniency Bias: Some raters are too generous and give high scores to everyone, regardless of their actual performance.
- Strictness Bias: On the other hand, some raters are very strict and consistently give low scores, even when performance is decent.
- Recency Bias: This happens when the rater’s evaluation is heavily influenced by the most recent behavior of the employee, overlooking their overall performance history.
- Spillover Effect: Past performance can significantly impact current performance appraisal. If someone performed well in the past, they may receive better marks, while those with past issues might receive lower scores, even if their current performance has improved.


