Functions of commercial banks Class 12 | Types of Banks
Functions of commercial banks Class 12
In this articles topics include:
- What is Commercial banking?
- What are the types of banks in India?
- What is the function of a commercial bank?
- Primary functions of commercial bank
- Secondary functions of commercial bank
BANKING
- The term bank comes from the French word ‘Banco’ which means a bench.
- A bank is a financial institution which deals with deposits and advances and other related services.
- The Indian Banking Regulation Act, 1949 defines “accepting for the purpose of lending or investment, of deposits of money from the public, repayable on demand or otherwise, and withdrawable by cheque, draft order or otherwise.
Types of Banks
Central Bank: – The central bank is the apex (Top) financial institution in the country. In India, the central bank is the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). It was established in 1935 in India under the Reserve Bank of India, Act 1934. The main function of RBI is to bring Economic Development. This bank issues currency controls to other banks and works as a bank of the government. And RBI also guides other banks.
Commercial Banks:– Commercial banks play a very important role in the economic and social development of a country. The commercial banks perform important functions such as :
- Primary functions, accepting deposits from the public and lending money.
- A secondary function is agency functions and utility functions.
In India, commercial banks can be divided into three groups.
- Public sector bank: a total of 26 banks such as state bank of India, Bank of Baroda, Dena Bank, Bank of India.
- Private sector banks such as AXIS bank, ICICI Bank, HDFC Bank, etc.
- Foreign Banks operating in India such as HSBC, Citi Bank, Standard Chartered Bank, etc.
Co-operative Banks:– Co-operative Banks are financial institutions registered under the co-operative societies Act. The main objective of cooperative banks is to provide credit to economically backward people, farmers, and small-scale units. The co-operative banks encourage saving habits in villages and also provide loans at low interest.
Savings Bank: – This bank accepts small saving from the public in rural areas. It encourages saving habits in villages. Examples are the postal savings bank. Commercial and Co-operative banks also encourage savings of the people.
Specialized Bank: – Some banks specialize in certain areas to provide finance either directly or indirectly. Some of these banks include:
- EXIM Bank: It is Exporter and Importer Bank of India was set up in 1982 to provide medium and long-term finance to exporters and importers.
- SIDBI: Small Development Bank of India was set up in 1990 to provide medium and long-term finance to small industries.
- NABARD: The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development was set up in 1982. It is the apex bank financing agriculture and rural development.
Exchange Bank: – The main aim of an Exchange bank is financing foreign trade. The main function of exchange banks are:
- Financing foreign trade transactions.
- Discounting of foreign bills of exchange.
- Issue of letter of credit.
- Remitting money from one country to another.
Development Banks: – These are the financial institutions that provide medium and long-term finance to the business organization. Examples are, Industrial Corporation of India (IFCI), State Financial Corporation (SFC), etc.
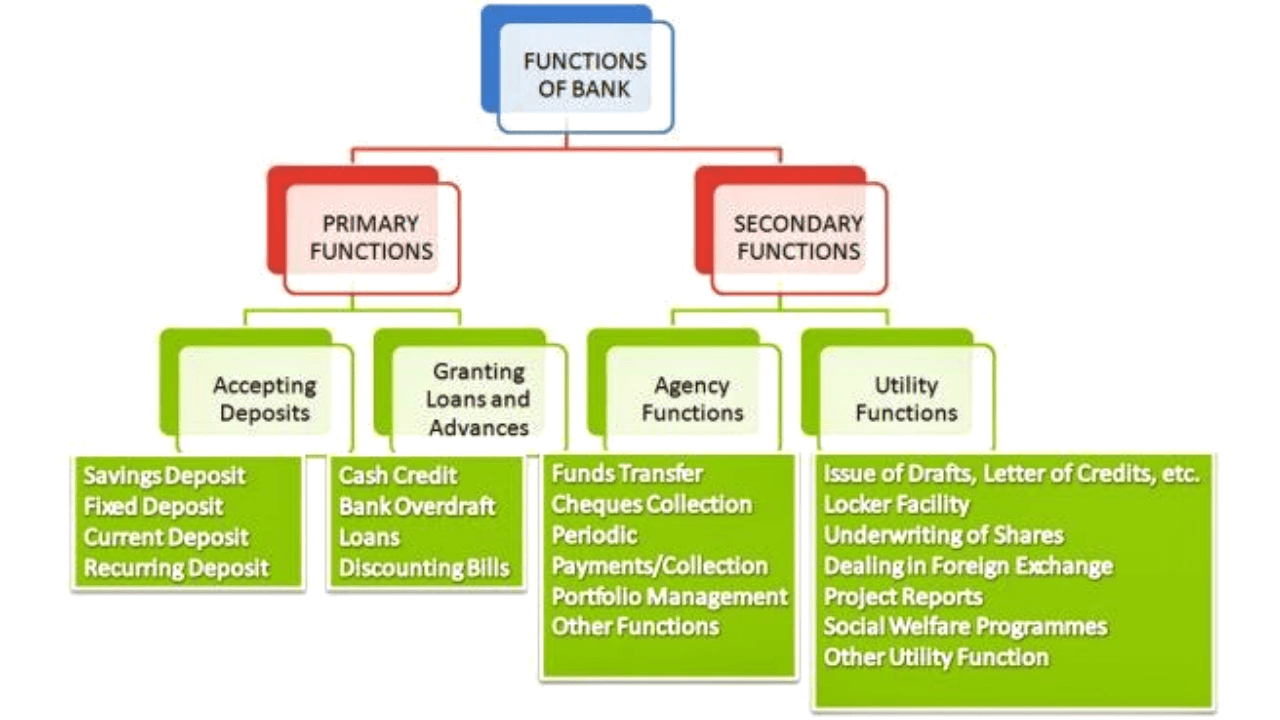
The primary function of a commercial bank
A) Accepting Deposit: –This is one of the main functions of every bank. The bank collects deposits from the public. The deposit can be of different types such as:
- Savings deposit
- Current Deposits
- Fixed Deposits
- Recurring Deposits
- Savings Deposits: – It encourages saving habits among the people. The rate of interest is low. At present, it is about 3.5% p.a. this account is suitable for salary and wages earners.
- Fixed Deposits:-Under this account, money is deposited for a certain fixed period. A higher rate of interest is paid. Depositors can keep for a period ranging from 15days to 5 years or more.
- Current Deposits: –This type of account is operated by businessmen. Withdrawals are freely allowed. The account holders can get the benefit of an overdraft facility.
- Recurring Deposits:-It is operated by salaried persons and small traders. A certain sum of money is periodically deposited into the bank. Withdrawals are permitted only after the expiry period. A higher rate of interest is paid.
B) Granting of Loans and Advances: –The bank advances loans to the business community and other members of the public. The bank loans advances include:
-
- Overdraft
- cash Credits
- Loans
- Discounting of bills of exchange.
- Overdraft: it is given to current account holders. Interest is charged only on the used amount. It is provided to business and non-business organizations.
- Cash Credits: Under this account, the customer can borrow a certain limit against security. A separate A/c is opened in the name of the borrower and the amount sanctioned is credited to this A/c. Interest is charged on the amount withdrawn.
- Loans:- Bank provides loans for the short term say a period of one year and medium term say a period of five years. Nowadays, banks do lend money for long period. Repayment of money can be in the form of installments spread over a period of time. The rate of interest depends upon, the amount of the loan and the period of the loan.
- Discounting of Bill of Exchange: – The bank provides funds to their customers by purchasing or discounting bills of exchange. The bank charges commission or interest up to the maturity period of the bills.
Secondary functions:
Agency functions: The bank acts as an agent of its customers. The bank performs agency functions. Which includes:
- Transfer of funds: The bank transfers funds from one bank to another bank or one place to another.
- Collection of cheques: The bank collects money from the bill of exchange. The bank also collects the money of the Cheques of its customers through the clearing section.
- Periodic Payment: The commercial bank makes the periodic payment in respect of electricity, bills, rent, etc. on the behalf of its customers.
- Portfolio Management: The commercial bank purchase and sell the shares and debentures on the behalf of its customers. This facility is called portfolio management.
- Periodic collection: the bank collects the salary, pension, dividend, and other periodic collections on the behalf of its customer.
- Other agency functions: it acts as a trustee on the behalf of its customer. And it also Acts as a foreign exchange transaction.
General Utility Functions: The bank also performs general utility functions, such as :
- Locker facility: the commercial bank provides a locker facility for safe custody and valuable documents.
- Underwriting of Shares: the bank underwrites shares and debentures through its merchant banking division.
- Issue of the draft, Letter of Credits, etc.: Bank issues draft for transferring of money from one place to another. It also issues a letter of credit, in case of import.
- Dealing foreign exchange: Commercial banks are allowed by RBI to deal in foreign exchange.
- Project report: The bank may also undertake to prepare project reports and feasibility studies on behalf of its clients.
- Other Utility functions: It provides market information to its customers etc.
Economics Notes Click Here
Reference infoendless, Mumbai University books (IDOL)
Functions of commercial banks Class 12, types of banks, tybcom business economics, Functions of Commercial Banks : -primary and secondary functions of banks